
AI Voice Detection and Music: Protecting Against Synthetic Audio Threats
The ability to clone voices and generate music with AI has exploded in recent years. What started as a novelty—like making a celebrity say something funny—has evolved into a serious security and trust threat. Today, anyone with an internet connection can access powerful AI voice cloning or music generation tools. With just a few seconds of audio sample, a person’s voice can be replicated by an ai model to say anything, in any language or style. On the music side, ai models can pump out songs in the style of real artists, complete with convincing vocals and instrumentals.
The result? Synthetic audio is becoming cheap, fast, and widely accessible, moving from harmless demos to real-world abuse. The difference between AI-generated and human-created music is becoming harder to notice, as sophisticated AI makes it challenging for listeners to tell them apart without specialized tools. Some listeners even find AI-generated audio weird or uncanny, especially when subtle human elements are missing. For example, synthetic voices often lack the micro-pauses and natural breathing sounds present in human speech.
This post explores how AI-generated voice and music are being misused, why humans (and legacy tools) can’t reliably catch it anymore, and how AI-powered detection is stepping up as an essential defense.
The Rise of Synthetic Audio Threats
Not long ago, producing a believable fake voice or song required extensive expertise and expensive software. Now AI voice cloning is essentially an off-the-shelf service. A plethora of companies and open-source tools offer the ability to create cloned voices on demand. In fact, modern algorithms can recreate a unique voice with as little as 3 seconds of recorded audio. With 10–30 seconds of someone’s voice, attackers can capture even subtle vocal quirks. This dramatic lowering of the barrier means that what once took a studio of experts can now be done by a casual user or a small team with a modest budget. The technology has also become incredibly fast – some AI models can generate cloned speech almost in real time.
On the music front, generative AI models have learned to compose in various genres, mimic famous singers, and even master the production style of hit songs. These models can also help artists create music by generating melodies, supporting vocals, or collaborating with AI personas. The internet is now flooded with AI-generated tracks that sound uncannily human. One major streaming platform found that about 18% of the tracks uploaded each day were fully AI-generated. Most of these don’t go viral, but tellingly, many were uploaded in an attempt to game the system – over 70% of those AI songs’ streams were fake, likely auto-played by bots to farm royalties. Most people can still identify AI-generated music when it is less sophisticated, but as the technology advances, it becomes harder for the average listener to tell the difference. AI-generated music often follows generic verse-chorus structures and may lack the emotional depth found in human-created music.
Where Synthetic Audio Causes Real Damage
AI-generated audio is far from harmless. It’s now being weaponized in various malicious ways, causing real-world harm across different domains. Key areas of concern include:
- Financial Fraud & Impersonation Scams: Perhaps the most immediate threat is scammers cloning voices to con people. Criminals have used AI voice clones to impersonate company CEOs and trick employees into authorizing large wire transfers. Attackers may also target user accounts, attempting to gain unauthorized access or take over accounts using AI-generated voices. In response, some platforms are implementing stricter account management policies, including options to delete an account or enhance authentication.
- Fake Customer Support & Phone Scams: Imposters are also cloning voices of legitimate representatives or public figures to lend credibility to scams. Imagine receiving a call from “your bank’s fraud department” and it truly sounds like the officer you spoke with last month. Fraudsters have used AI to mimic call center agents, tech support staff, or government officials to extract sensitive data or payments. Such voice phishing (vishing) has become harder to spot as the cloned voices mirror the tone and accent victims expect. In high-security sectors, real-time liveness detection is now used to prevent deepfake-based account takeovers, adding an extra layer of protection against these sophisticated attacks.
- Copyright Violations & Fake Music Releases: The music industry is alarmed by a wave of AI-generated tracks that mimic real artists. In a well-known incident, an anonymous creator released an AI-generated song featuring the cloned voices of famous musicians (Drake and The Weeknd) which garnered millions of streams before it was caught and removed. Beyond such viral hits, there’s a quieter flood of AI-made tracks uploaded to streaming platforms under fake artist names, hoping to collect royalties or piggyback on popular styles.
- Disinformation & Reputational Harm: Just as deepfake videos can spread disinformation, AI-generated audio poses a looming threat to politics and public trust. Fake audio clips of public figures saying things they never said can be weaponized to influence opinion or tarnish reputations. For instance, a forged audio recording of a politician discussing a scandal could be released during an election, with the realistic clone of their voice making it believable. In the age of social media, such an audio deepfake can go viral before it’s debunked.
- Platform Trust Erosion & Regulatory Exposure: If synthetic audio abuse runs unchecked, online platforms risk losing user trust at a fundamental level. Whether it’s fake voice notes on a chat app or AI music flooding a content library, users will start to question if anything they hear is real. This, in turn, puts companies in the crosshairs of regulators.
Why Human Detection No Longer Works
Given these threats, why not simply listen for what’s real or fake? The trouble is human ears can no longer be trusted to detect AI-generated audio. Early deepfake voices often had telltale signs – odd cadences, robotic tones – but today’s cloned voices can be virtually indistinguishable from a natural speaker. A recent survey found 70% of people aren’t confident they could tell a cloned voice from the real thing. This isn’t because people are naive; it’s because the forgeries have gotten that good. AI voices can inject emotion, breathing sounds, and nuanced inflection. Likewise, AI-generated music can feature highly realistic instruments and vocals that even seasoned listeners might assume were human-produced. There are no obvious glitches for an average person to pick up on, especially if they’re not actively suspicious.
Technical approaches like human voice detection attempt to distinguish AI-generated speech from genuine human speech by analyzing indicators such as pitch variation, pauses, and background noise to determine authenticity. Additionally, voice biometrics analyze unique vocal characteristics for secure authentication, a technology commonly used in banking.
Furthermore, the speed and scale of the problem overwhelm any manual effort. Imagine a social media platform trying to screen millions of videos, audio clips, and songs uploaded daily – it’s impossible to have human moderators listen to each one. Banks and call centers receive countless customer calls; a fraudster slipping in an AI-voiced call among thousands of legitimate ones won’t be caught by a rep just “hearing something off.” Traditional tools like simple audio fingerprinting or rule-based systems fall short too, because they can’t easily distinguish a skilled deepfake from genuine audio.
How AI Voice Detection Works (High-Level)
To fight synthetic audio, AI-powered detection systems have been developed that analyze sound in ways far more granular than human hearing. These detectors, often referred to as an ai detection tool, employ advanced signal processing and machine learning models to pick up subtle artifacts in speech audio that often accompany AI generation. For example, while a person might focus on what is being said, a detector algorithm scrutinizes how it’s being said: the micro-level patterns in pitch, timing, and harmonics. Authentic human speech has natural variations in tone and flow – tiny fluctuations as we breathe or emphasize words. AI-generated speech may lack some of this organic randomness.
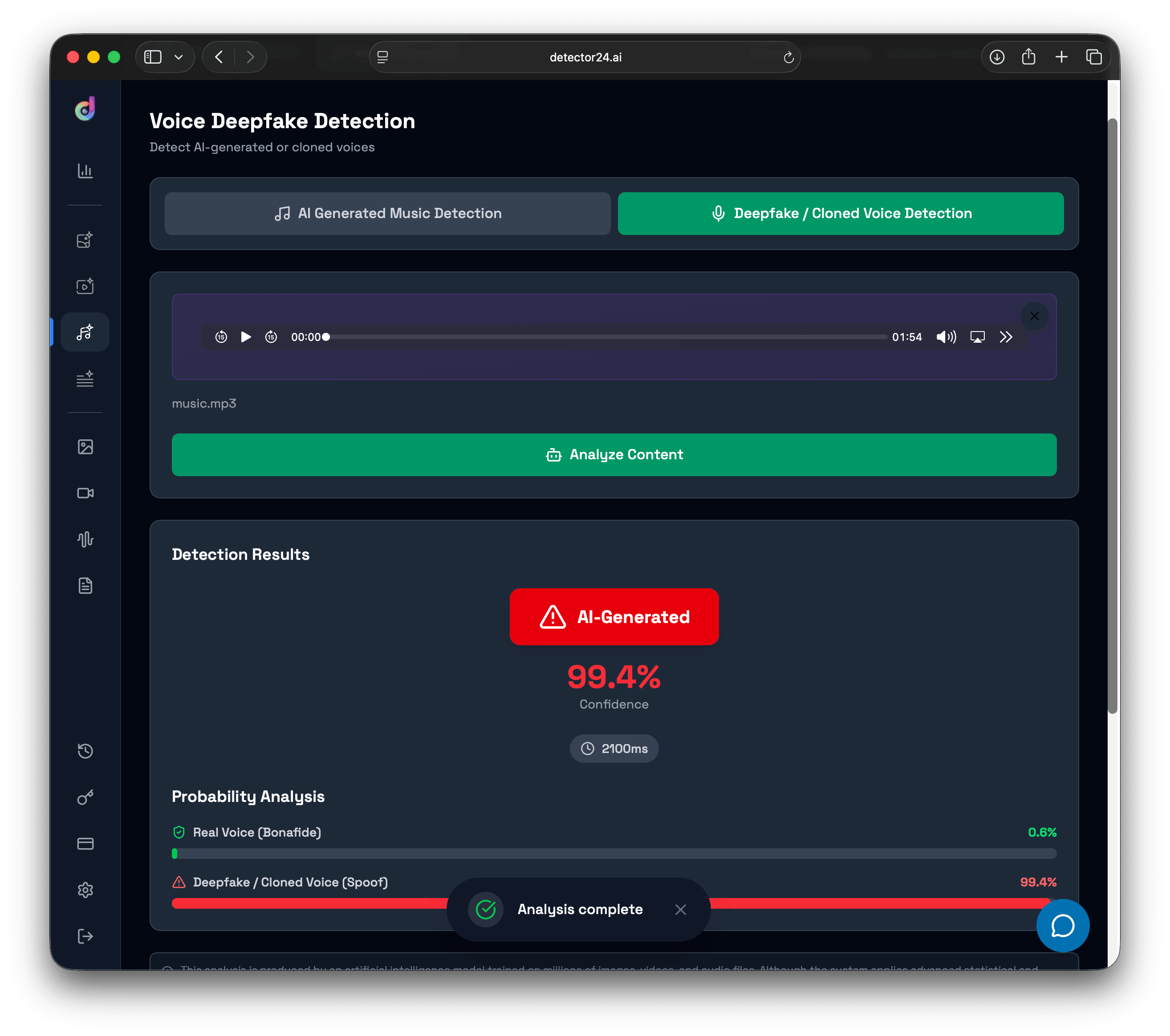
Modern voice deepfake detectors often work by converting audio into visual or mathematical representations (like spectrograms that map frequency over time) and feeding those into neural networks. The AI looks for the “fingerprints” of synthesis: for instance, certain digital noise or cutoff frequencies left by the generation process, or inconsistencies in how formants (the resonance frequencies of human vocal tracts) appear. By comparing these features against what it has learned from large datasets of real vs fake audio, the detector can output a probability that a given voice sample is AI-generated.
Crucially, AI voice detection can be deployed in different modes depending on the use case. In real-time scenarios, such as monitoring a live phone call or video conference, lightweight models analyze incoming audio on the fly and raise an alert if the voice is likely fake. Many detection models can run directly on devices, providing near-instant results without sending audio data to the cloud. (Some solutions claim to flag a deepfake voice within just a couple of seconds of speech!). For post-processing scenarios, like scanning uploaded videos or recorded calls, more intensive analysis can be run since there’s no rush to decide in milliseconds.
Key Features of AI Voice Detectors
Modern AI voice detectors are packed with advanced features designed to accurately identify AI-generated voices in a wide range of scenarios. At the heart of these tools is their ability to analyze intricate speech patterns, tone, and the overall structure of audio to determine whether a voice is human or AI-generated. By leveraging powerful machine learning algorithms, the AI voice detector compares the unique characteristics of an audio file against a vast library of known synthetic voice models. This process results in a clear probability score, giving users a straightforward indication of how likely it is that a voice is AI-generated.
One of the standout key features of today’s AI voice detectors is their support for multiple languages and accents. This makes them highly effective for global users, ensuring that detection is accurate whether the audio is in English, Spanish, Mandarin, or any other language. The ability to detect AI-cloned voices—those created to mimic real people—adds another layer of protection, especially as these fake voices become more common in scams and impersonation attempts.
Convenience is also a priority. Most AI voice detectors can process a variety of audio formats, including WAV, MP3, M4A, and OGG, without the need for file conversion or user login. This flexibility allows users to quickly upload and analyze audio, whether it’s a short speech, a voicemail, or a longer recording. By combining robust speech analysis, multi-language support, and user-friendly design, AI voice detectors are becoming an essential tool for anyone looking to detect AI-generated voices and protect against synthetic audio threats.
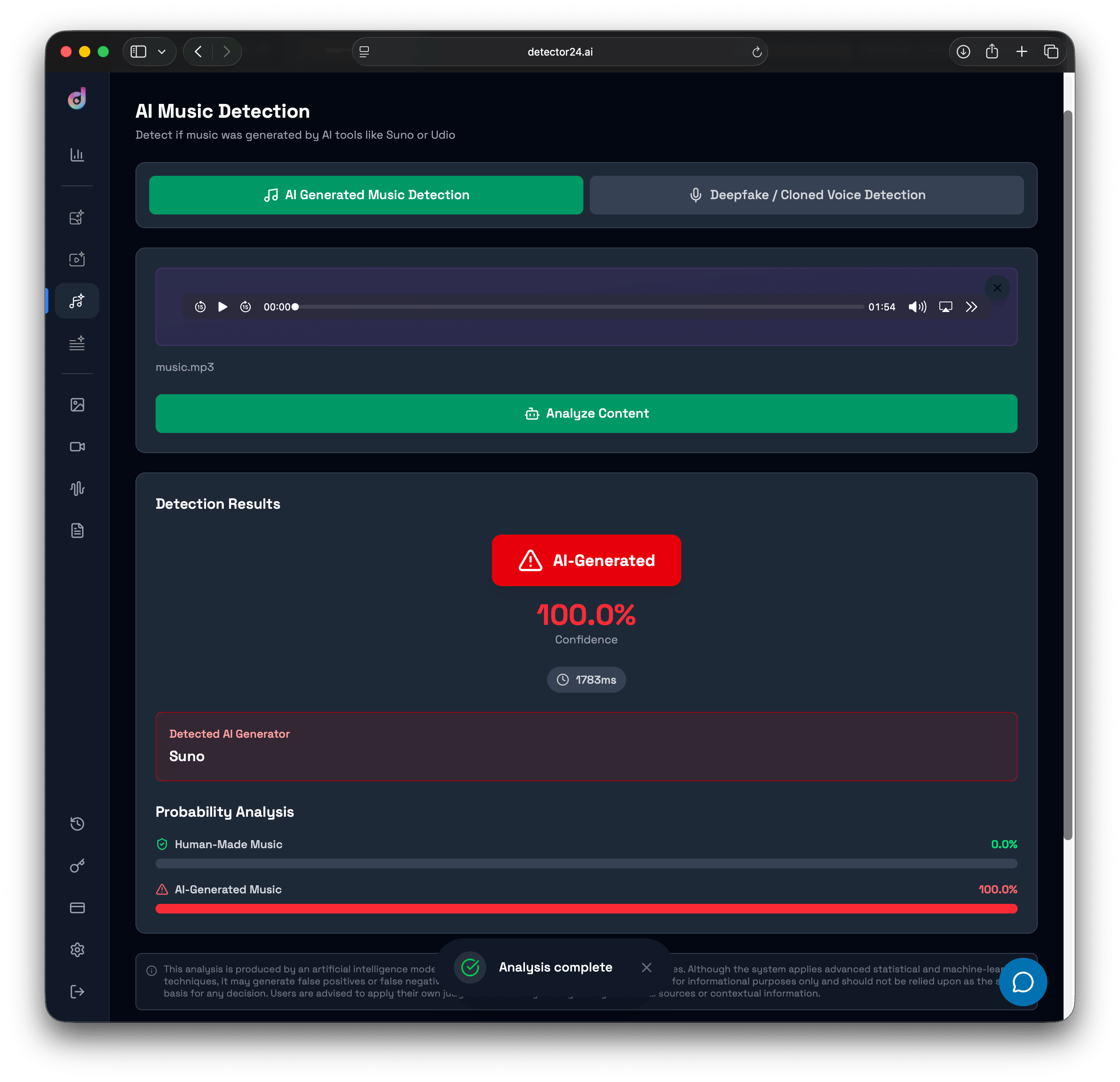
How AI Music Detection Works
Detecting AI-generated music presents its own challenges, but similar principles apply. Music detectors use a mix of signal analysis and machine learning to find the subtle cues that differentiate human-made music from AI compositions. Some telltale signs include:
- Spectral Artifacts & Timbre Fingerprints: AI music often has unnatural frequency artifacts or an overly “perfect” sound in certain bands. For example, many generative models rely on neural vocoders that can leave slight spectral fingerprints – tiny distortions like quantization noise or aliasing in the high frequencies. A human recording, in contrast, might have a bit of analog hiss, microphone quirks, or varied texture in the sound. Detectors compute audio features (such as spectral flatness or roll-off) to catch a track that’s too clean or has oddly uniform frequency distribution.
- Consistency vs Human Imperfections: Human performances have irregularities – a drummer might speed up or slow down by a few milliseconds, a singer’s volume wavers with emotion, a guitarist might not hit every note at exactly the same intensity. AI-generated music, however, can be too consistent. It might have perfectly quantized rhythm and uniform dynamics that make it sound mechanically precise. Listeners often describe AI-generated performances as having a sterile, soulless quality due to this lack of micro-variation.
- Harmonies and Musical Nuance: AI-generated music may produce unnatural or ghost harmonies that appear and disappear unexpectedly, which can be a giveaway compared to the more organic harmonies found in music by a real person.
- Structural and Creative Oddities: While harder to catch automatically, AI-composed music might show structural patterns that seem off to an experienced ear. Lyrics might be grammatically correct yet oddly generic or repetitious. A song could have looping sections or key changes that feel unnatural. Automated detectors focus mostly on the audio signal itself, but combined approaches (with some metadata or lyrical analysis) can flag these creative tells.
- Background Music Use: AI-generated background music is often used for casual listening or ambient settings, but it may lack the originality and creative spark that comes from human musicianship.
- AI-Created Bands and Projects: There have been cases of AI-created bands that gained attention for their lack of real social media presence, live performances, or personal interactions—highlighting the synthetic nature of the project and raising questions about authenticity and transparency in digital music creation.
- Partial AI Usage (Hybrids): A growing reality is music that’s partly AI-generated – e.g. a human producer uses an AI tool for the drumline or to generate a draft melody which they then build upon. This makes detection trickier, as the song isn’t fully synthetic. Advanced detection frameworks tackle this by separating a track into stems (vocals, drums, instruments) and analyzing each individually. It might find, say, the instrumental is likely AI-generated but the vocals are human. The result could be a spectrum or **confidence score (like 0 to 10)**indicating how much AI is present in different parts of the music.
It is increasingly important to distinguish whether a song or artist is a real person or AI-generated, especially as AI-driven projects become more common in the music industry. Experts disagree on whether AI-generated music represents a threat or an opportunity for musicians, and there is currently no legal obligation for streaming platforms to label AI-generated songs.
Building robust AI music detectors requires large and diverse training data – they need to learn the nuances of many genres, production styles, and also the quirks of various AI music models. Over time, as generative music tools improve, detectors are continuously retrained to catch new fingerprints left by the latest algorithms. It’s very much an arms race, but the goal is clear: to ensure authenticity in music so that when you press play, you know whether you’re hearing a human artist or a machine, especially when it concerns copyright and artist reputations.
The Importance of Transparency in AI Music
As AI-generated music becomes a regular feature on streaming platforms, transparency has never been more important in the music industry. Listeners deserve to know whether the track they’re enjoying was created by a human artist or generated by AI. Clear labeling of AI-generated music helps build trust between artists, streaming platforms, and fans, ensuring that everyone understands the origins of the music they’re listening to.
Transparency also plays a crucial role in protecting the rights of human artists. By tagging AI-generated tracks and providing detailed metadata, streaming platforms can prevent confusion, reduce the risk of copyright disputes, and help listeners make informed choices. Companies like Deezer are already leading the way by launching AI detection tools and implementing tagging systems for AI-generated music, setting a standard for the industry.
Ultimately, transparency fosters a more honest and open music ecosystem. It allows human artists and AI-generated music to coexist fairly, giving credit where it’s due and ensuring that the music industry remains a place where creativity and innovation are respected. As AI continues to shape the future of music, clear communication about what’s human and what’s generated will be key to maintaining trust and integrity in the industry.
Where AI Audio Detection Is Used
Given the wide range of threats, AI voice and music detection is being adopted across industries and platforms as a crucial part of the security and trust toolkit. AI voice detection technology is now widely used in personal virtual assistants, customer service automation, voice biometrics, and real-time transcription services. Some of the key use cases include:
- Content Moderation on Platforms: Social networks, video-sharing sites, and audio streaming platforms are integrating AI detectors to scan user-uploaded content. This helps catch deepfake audio or AI-synthesized media before it spreads. In the music realm, major streaming services have begun labeling AI-generated tracks to be transparent with listeners and to ensure these tracks don’t slip into monetized playlists unknowingly. Streaming platforms like Deezer have launched AI detection tools to tag AI-generated music and prevent it from being recommended to users. Some AI voice detection tools, such as the one from Undetectable, are completely free to use and do not require user login, making them accessible for instant analysis.
- Fraud Prevention & Identity Verification: Banks, fintech firms, and enterprise security teams are turning to voice deepfake detection to combat impersonation fraud. As mentioned, fraudsters have started to target call centers and phone-based verifications with AI voices. Financial institutions now realize that a caller’s voice cannot be assumed genuine without checks. Major banks use voice biometrics to verify customers and detect synthetic voices during phone transactions. Some are deploying detection algorithms in their phone systems to spot suspect voices in real time, complementing traditional anti-fraud checks.
- Copyright Enforcement & Music Rights Management: Record labels, publishers, and streaming platforms use AI detection to police the influx of AI-made music for potential copyright issues. A detection system might scan new uploads and compare the vocal fingerprint to known artists – if it finds a match that suggests the vocals are a cloned version of, say, Taylor Swift’s voice, it can automatically flag that track for review. This is how unauthorized AI versions of songs or AI “covers” using an artist’s voice are being identified and taken down before they collect royalties illegally or confuse the market. Additionally, detection helps rights holders differentiate between a legitimately licensed sample versus an AI-generated imitation. AI can also help artists manage large volumes of fan messages and interactions, allowing them to focus on creativity.
- Telecommunications & Call Authentication: Telephony providers and secure communications services are looking at integrating voice deepfake detection to ensure the person on the other end of a call is real. This is particularly relevant for services like emergency dispatch, government hotlines, or high-value customer support where verifying identity is crucial. Some vendors offer real-time call monitoring tools that listen for AI-generated audio cues during calls (without interrupting the conversation) and can alert a security team if an impersonation is suspected. Enterprises are also using these tools internally to protect executive communications – for example, if a hacker tries to deepfake the CEO’s voice on a voicemail to an employee, the system would flag it. This kind of detection-as-a-service can dramatically reduce the success rate of voice phishing and impersonation attempts in organizations.
- Law Enforcement and Digital Forensics: Police and investigators have a growing need to authenticate audio evidence. AI audio detection is being used in forensic labs to analyze recordings and determine if they’ve been manipulated or generated by AI. In a courtroom scenario, an expert might run a suspect audio clip through detection software and testify that the voice has characteristics inconsistent with a real human (backed by acoustic analysis). This was science fiction not long ago, but it’s quickly becoming routine given cases where audio could be faked. Intelligence agencies and cybersecurity units similarly use detection to monitor disinformation campaigns – for example, catching a fake terrorist audio message or a bogus “leaked” recording before it incites violence or panic. Essentially, anywhere authenticity of audio is paramount, AI-based detectors are joining the front lines to help distinguish fact from fiction.
AI voice detection tools can analyze various audio formats, including MP3, WAV, M4A, and OGG, making them versatile for different use cases. To help users understand the differences between AI-generated and human voices, many platforms include an audio element (embedded audio player) so you can listen to voice samples side by side. Visual representations, such as the image below, further illustrate how AI-generated content can be detected and attributed.
Some leading AI voice detection tools have been featured by reputable media outlets and organizations, highlighting their credibility and industry recognition.
In summary, AI-generated voice and music bring amazing creative possibilities, but also very real dangers. As synthetic audio becomes ever more convincing, our collective ability to trust what we hear is under strain. However, through cutting-edge detection technology and sensible policies, we can restore a measure of trust. By understanding the threats and implementing AI-driven detectors to counter AI-driven fakes, organizations can protect themselves and their users from the worst of these new risks. The battle for audio authenticity is just beginning, and it’s one fight we cannot afford to tune out. There is hope among artists and industry stakeholders that AI will ultimately democratize music production and foster transparency, while responsible use and regulation can ensure a positive impact.
The Future of AI Voice and Music Detection
Looking ahead, the future of AI voice and music detection is set to be shaped by rapid advancements in machine learning and AI technology. As AI-generated music and voices become more widespread, the need for highly accurate and efficient detection tools will only increase. We can expect to see the development of even more sophisticated AI detection tools capable of identifying AI-generated content with remarkable precision, regardless of language, accent, or audio quality.
Integration of these detection tools into streaming platforms and music industry workflows will become standard practice, enabling real-time identification and labeling of AI-generated music and voices. This will not only help protect artists and listeners but also support a more transparent and trustworthy music industry. In addition, new applications for AI voice and music detection are likely to emerge, such as personalized music recommendations based on the authenticity of tracks, or the creation of more lifelike AI-generated voices for virtual assistants and entertainment.
Ultimately, the future of AI voice and music detection will be defined by the ongoing interplay between technological innovation, industry needs, and societal expectations. As detection tools become more advanced and widely adopted, they will play a crucial role in ensuring that the music industry remains fair, creative, and transparent—empowering users to identify and enjoy music and voices with confidence, no matter how they are generated.
Want to learn more?
Explore our other articles and stay up to date with the latest in AI detection and content moderation.
Browse all articles